EUROPE
Goals and values of the EU
Goals
The goals of the European Union are:
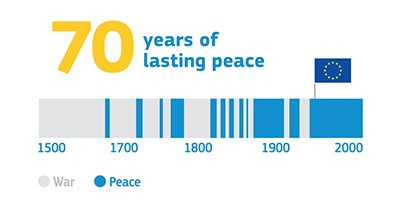
- promote peace, its values and the well-being of its citizens
- offer freedom, security and justice without internal borders
- sustainable development based on balanced economic growth and price stability, a highly competitive market economy with full employment and social progress, and environmental protection
- combat social exclusion and discrimination
- promote scientific and technological progress
- enhance economic, social and territorial cohesion and solidarity among EU countries
- respect its rich cultural and linguistic diversity
- Establish an economic and monetary union whose currency is the euro.
Values
The EU values are common to the EU countries in a society in which inclusion, tolerance, justice, solidarity and non-discrimination prevail. These values are an integral part of our European way of life:
- Human dignity
Human dignity is inviolable. It must be respected, protected and constitutes the real basis of fundamental rights. - Freedom
Freedom of movement gives citizens the right to move and reside freely within the Union. Individual freedoms such as respect for private life, freedom of thought, religion, assembly, expression and information are protected by the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights. - Democracy
The functioning of the EU is founded on representative democracy. Being a European citizen also means enjoying political rights. Every adult EU citizen has the right to stand as a candidate and to vote in elections to the European Parliament. EU citizens have the right to stand as candidate and to vote in their country of residence, or in their country of origin. - Equality
Equality is about equal rights for all citizens before the law. The principle of equality between women and men underpins all European policies and is the basis for European integration. It applies in all areas. The principle of equal pay for equal work became part of the Treaty of Rome in 1957. Although inequalities still exist, the EU has made significant progress. - Rule of law
The EU is based on the rule of law. Everything the EU does is founded on treaties, voluntarily and democratically agreed by its EU countries. Law and justice are upheld by an independent judiciary. The EU countries gave final jurisdiction to the European Court of Justice which judgements have to be respected by all. - Human rights
Human rights are protected by the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights. These cover the right to be free from discrimination on the basis of sex, racial or ethnic origin, religion or belief, disability, age or sexual orientation, the right to the protection of your personal data, and the right to get access to justice.
The EU in the world
Trade
The European Union is the largest trade block in the world. It is the world’s biggest exporter of manufactured goods and services, and the biggest import market for over 100 countries.
Free trade among its members was one of the EU’s founding principles. This is possible thanks to the single market. Beyond its borders, the EU is also committed to liberalising world trade.
Humanitarian aid
The EU is committed to helping victims of man-made and natural disasters worldwide and supports over 120 million people each year. Collectively, the EU and its constituent countries are the world’s leading donor of humanitarian aid.
Diplomacy and security
The EU plays an important role in diplomacy and works to foster stability, security and prosperity, democracy, fundamental freedoms and the rule of law at international level.
Source: europa.eu